Category
Description
Created 2024-12-20T23:47:47+00:00 by LN Anderson; Last updated 2025-05-09T15:55:34+00:00
S. elongatus PCC 7942 Circadian Control Bioproduction Metabolomics (PB-DP5)
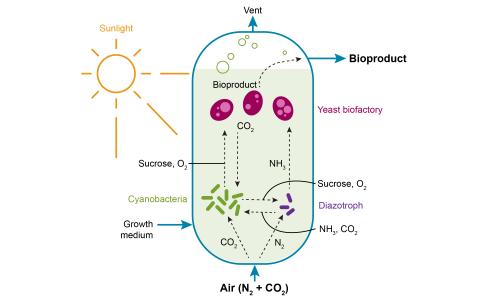
The purpose of this experiment was to evaluate how circadian clock regulation impacts carbon partitioning between storage, growth, and product synthesis in Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 in providing insights to strategies for enhanced bioproduction. Culture samples (8 mL) were collected at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours for extracellular sucrose analysis. Sample data was acquired using a Agilent single quadrupole gas chromatography-mass spectrometer and processed using Agilent Mass Hunter for targeted sucrose quantification. Metabolomic targeted analysis of PCC 7942 light-dark cycle cultures transitioned to constant light revealed distinct temporal patterns in sucrose production.
Accessible Digital Data Downloads
Processed metabolomic datasets are openly accessible from the download button and contain targeted sucrose quantification results files and supporting metadata materials for increased data transparency and reuse.
Data Download Reference Citations
- Anderson, Lindsey N, Johnson, Zachary D, Waters, Katrina M, & Bohutskyi, Pavlo (2024). PPI DataHub Project Data Package: S. elongatus PCC 7942 Circadian Control Bioproduction Metabolomics (PB-DP5). United States. 2024. PNNL DataHub (Web). DOI: 10.25584/2510499
- Gilliam, A., Sadler, N. C., Li, X., Garcia, M., Johnson, Z., Veličković, M., Kim, Y. M., Feng, S., Qian, W. J., Cheung, M. S., & Bohutskyi, P. (2025). Cyanobacterial circadian regulation enhances bioproduction under subjective nighttime through rewiring of carbon partitioning dynamics, redox balance orchestration, and cell cycle modulation. Microbial cell factories, 24(1), 56. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02665-5
Linked Primary Data
Primary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) raw measurement data are openly accessible for download at the Mass Spectrometry Interactive Virtual Environment (MassIVE) community repository under the accession MSV000096722.
Funding Acknowledgments
The research data described here was funded in whole or in part by the Predictive Phenomics Initiative (PPI) at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL). This work was conducted under the Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program at PNNL. PNNL is a multiprogram national laboratory operated by Battelle for the DOE under Contract No. DE-AC05-76RL01830.
Citation Policy
In efforts to enable discovery, reproducibility, and reuse of PPI-funded project dataset citations in accordance with best practices (as outlined by the FORCE11 Data Citation Principles), we ask that all reuse of project data and metadata download materials acknowledge all primary and secondary dataset citations and corresponding journal articles where applicable.
Data Licensing