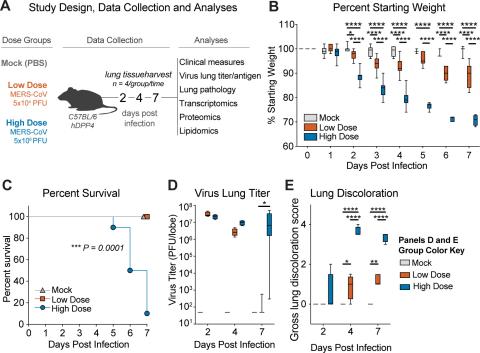
Coronaviruses (CoV) emerge suddenly from animal reservoirs to cause novel diseases in new hosts. Discovered in 2012, the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is endemic in camels in the Middle East and is continually causing local outbreaks and epidemics. While all three newly emerging human CoVs from the past 20 years (SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and MERS-CoV) cause respiratory disease, each CoV has unique host interactions that drive differential pathogeneses. To better understand the virus and host interactions driving lethal MERS-CoV infection, we performed a longitudinal multi-omics analysis of sublethal and lethal MERS-CoV infection in mice. Significant differences were observed in body weight loss, virus titers, and acute lung injury among lethal and sub-lethal virus doses. Virus-induced apoptosis of type I and II alveolar epithelial cells suggests that loss or dysregulation of these key cell populations was a major driver of severe disease. Omics analysis suggested differential pathogenesis was multi-factorial with clear differences among innate and adaptive immune pathways as well as those that regulate lung epithelial homeostasis. Infection of mice lacking functional T and B cells showed that adaptive immunity was important in controlling viral replication but also increased pathogenesis. In summary, we provide a high-resolution host response atlas for MERS-CoV infection and disease severity. Multi-omics studies of viral pathogenesis offer a unique opportunity to not only better understand the molecular mechanisms of disease but also to identify genes and pathways that can be exploited for therapeutic intervention all of which is important for our future pandemic preparedness.
Reference Citation
Sims, Amy C et al. “Dysregulation of lung epithelial cell homeostasis and immunity contributes to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease severity.” mSphere, e0095124. 30 Jan. 2025, doi:10.1128/msphere.00951-24
Projects (1)
Last updated on 2024-02-11T22:41:43+00:00 by LN Anderson PNNL DataHub NIAID Program Project: Modeling Host Responses to Understand Severe Human Virus Infections, Multi-Omic Viral Dataset Catalog Collection Background The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) "Modeling Host...
Category
Datasets
45