The data accompanies the manuscript in review that evaluates salinity-associated shifts in organic C thermodynamics, biochemical transformations, and heteroatom content in a first-order coastal watershed in the Olympic Peninsula of Washington state, USA. The files contain raw data including soil...
Filter results
Category
- (-) Earth System Science (167)
- (-) Human Health (113)
- Scientific Discovery (404)
- Biology (287)
- Integrative Omics (96)
- Microbiome Science (50)
- National Security (32)
- Computational Research (25)
- Computing & Analytics (18)
- Energy Resiliency (14)
- Chemical & Biological Signatures Science (12)
- Weapons of Mass Effect (12)
- Materials Science (11)
- Chemistry (10)
- Data Analytics & Machine Learning (9)
- Renewable Energy (8)
- Computational Mathematics & Statistics (7)
- Data Analytics & Machine Learning (7)
- Atmospheric Science (6)
- Ecosystem Science (6)
- Visual Analytics (6)
- Coastal Science (4)
- Energy Storage (4)
- Plant Science (4)
- Solar Energy (4)
- Bioenergy Technologies (3)
- Energy Efficiency (3)
- Transportation (3)
- Cybersecurity (2)
- Distribution (2)
- Electric Grid Modernization (2)
- Grid Cybersecurity (2)
- Subsurface Science (2)
- Water Power (2)
- Wind Energy (2)
- Advanced Lighting (1)
- Computational Mathematics & Statistics (1)
- Environmental Management (1)
- Federal Buildings (1)
- Geothermal Energy (1)
- Grid Analytics (1)
- Grid Energy Storage (1)
- High-Performance Computing (1)
- Terrestrial Aquatics (1)
- Vehicle Technologies (1)
- Waste Processing (1)
Tags
- Virology (77)
- Immune Response (51)
- Time Sampled Measurement Datasets (51)
- Differential Expression Analysis (46)
- Gene expression profile data (45)
- Homo sapiens (42)
- Mass spectrometry data (31)
- Multi-Omics (31)
- Viruses (27)
- Omics (24)
- Soil Microbiology (24)
- Health (23)
- Virus (23)
- MERS-CoV (19)
- Mus musculus (18)
- sequencing (13)
- West Nile virus (13)
- Mass Spectrometry (12)
- Genomics (11)
- Influenza A (11)
- Metagenomics (10)
- Ebola (9)
- Predictive Phenomics (9)
- High Throughput Sequencing (8)
- Microbiome (8)
- Microarray (7)
- Type 1 Diabetes (7)
- Fungi (6)
- Imaging (6)
- Proteomics (6)
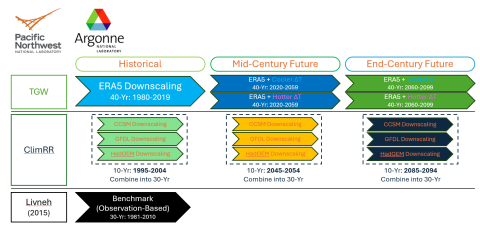
Problem Statement and Objectives : Climate datasets are available across many institutions. Understanding which one to use, or how to combine the datasets, and for which application, or/and which region, and/or which specific fundamental science question is a challenge. A multi-lab PNNL-ANL...
Category
Datasets
0
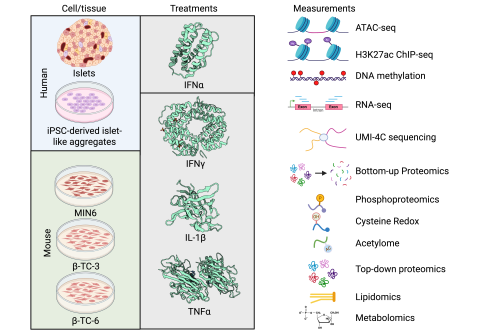
Background In type 1 diabetes (T1D), autoimmune response and inflammation cause the death of pancreatic β cells, leading to the body’s inability to produce insulin and maintain glucose homeostasis. This process is at least in part mediated by pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interferon (IFN)α...
Category
Datasets
21
Current methods for supply chain inventory data often require significant time and effort from manufacturers to compile. Additionally, without a uniform methodology these can result in inconsistent datasets that are difficult for practitioners to evaluate and compare, even within similar product...
Category
Datasets
3
Coronaviruses (CoV) emerge suddenly from animal reservoirs to cause novel diseases in new hosts. Discovered in 2012, the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is endemic in camels in the Middle East and is continually causing local outbreaks and epidemics. While all three newly...
Category
The ability of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) to promote cellular cholesterol efflux is a more robust predictor of cardiovascular disease protection than HDL-cholesterol levels in plasma. Previously, we found that lipidated HDL containing both apolipoprotein A-I (APOA1) and A-II (APOA2) promotes...
Category
Climate change is expected to increase the frequency of hotter and more intense droughts accompanied by aberrant precipitation events. Such extreme environmental shifts can trigger a complex cascade of microbial physiological responses that can impact the microbial community structure and functions...
Category
Please cite as: Graham E.B., and K.S. Hofmockel. 2021. "Ecological stoichiometry as a foundation for omics-enabled biogeochemical models of soil organic matter decomposition." Biogeochemistry 157. doi:10.1007/s10533-021-00851-2 Coupled biogeochemical cycles drive ecosystem ecology by influencing...
Category
Soil viruses are highly abundant and have important roles in the regulation of host dynamics and soil ecology. Climate change is resulting in unprecedented changes to soil ecosystems and the life forms that reside there, including viruses. In this Review, we explore our current understanding of soil...
Category
Metagenomics is unearthing the previously hidden world of soil viruses. Many soil viral sequences in metagenomes contain putative auxiliary metabolic genes (AMGs) that are not associated with viral replication. Here, we establish that AMGs on soil viruses actually produce functional, active proteins...
Category
Abstract Microbial response to changing environmental factors influences the fate of soil organic carbon, and drought has been shown to affect microbial metabolism and respiration. We hypothesized that the access of microbes to different carbon pools in response to dry–rewet events occurs...
Category
ABSTRACT Fungal mineral weathering regulates the bioavailability of inorganic nutrients from mineral surfaces to organic matter and increase the bioavailable fraction of nutrients. Such weathering strategies are classified as biomechanical or biochemical. In the case of fungal uptake of mineral...
Category
The soil microbiome’s role in regulating biogeochemical processing is critical to the cycling and storage of soil organic carbon (C). The function of the microbiome under different land management uses has become a focal area of research due to the interest in managing soil C to mitigate climate...
Category
Introduction: Understanding how microorganisms within a soil community interact to support collective respiration and growth remains challenging. Here, we used a model substrate, chitin, and a synthetic Model Soil Consortium (MSC-2) to investigate how individual members of a microbial community...
Category
ABSTRACT Climate change is causing an increase in drought in many soil ecosystems and a loss of soil organic carbon. Calcareous soils may partially mitigate these losses via carbon capture and storage. Here, we aimed to determine how irrigation-supplied soil moisture and perennial plants impact...