Metabolite exchange between plant roots and their associated rhizosphere microbiomes underpins plant growth promotion by microbes. Sorghum bicolor is a cereal crop that feeds animals and humans and is used for bioethanol production. Its root tips exude large amounts of a lipophilic benzoquinone...
Filter results
Category
- Biology (51)
- Scientific Discovery (51)
- Human Health (31)
- Earth System Science (13)
- Microbiome Science (10)
- Computational Research (5)
- Data Analytics & Machine Learning (5)
- Integrative Omics (4)
- Chemistry (1)
- Computational Mathematics & Statistics (1)
- Computational Mathematics & Statistics (1)
- Computing & Analytics (1)
- Data Analytics & Machine Learning (1)
- National Security (1)
- Plant Science (1)
Content type
Tags
- (-) Viruses (28)
- (-) PerCon SFA (10)
- (-) Machine Learning (7)
- Virology (77)
- Immune Response (51)
- Time Sampled Measurement Datasets (50)
- Differential Expression Analysis (46)
- Gene expression profile data (45)
- Homo sapiens (34)
- Mass spectrometry data (31)
- Multi-Omics (30)
- Omics (26)
- Health (23)
- Soil Microbiology (23)
- Virus (23)
- MERS-CoV (18)
- Mus musculus (18)
- Mass Spectrometry (14)
- Synthetic (14)
- Genomics (13)
- sequencing (13)
- West Nile virus (13)
- Influenza A (11)
- Metagenomics (10)
- Ebola (9)
- High Throughput Sequencing (9)
- Microbiome (8)
- Proteomics (8)
- Microarray (7)
- Synthetic Biology (7)
Short Biography Caroline (Carrie) Harwood received her Ph.D. in microbiology from the University of Massachusetts and completed postdoctoral work at Yale University. She held academic appointments at Cornell University and the University of Iowa before moving to the University of Washington in 2005...
Category
The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study is searching for factors influencing the development of type 1 diabetes (T1D) in children. Research has shown that there are certain genes that correlate to higher risk of developing T1D, but not all children with these genes...
Datasets
1
The Diabetes Autoimmunity Study in the Young (DAISY) seeks to find environmental factors that can trigger the development of type 1 diabetes (T1D) in children. DAISY follows children with high-risk of developing T1D based on family history or genetic markers. Genes, diets, infections, and...
Datasets
1
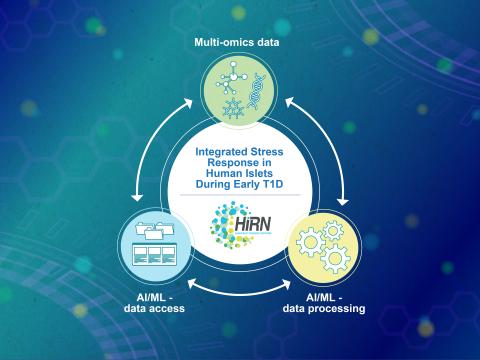
Machine learning is a core technology that is rapidly advancing within type 1 diabetes (T1D) research. Our Human Islet Research Network (HIRN) grant is studying early cellular response initiating β cell stress in T1D through the generation of heterogenous low- and high-throughput molecular...
Datasets
3
Elmore JR, Dexter GN, Baldino H, Huenemann JD, Francis R, Peabody GL 5th, Martinez-Baird J, Riley LA, Simmons T, Coleman-Derr D, Guss AM, Egbert RG. High-throughput genetic engineering of nonmodel and undomesticated bacteria via iterative site-specific genome integration. Sci Adv. 2023 Mar 10;9(10)...
PerCon SFA, Co-Investigator Vivian Lin earned her PhD in organic chemistry from the University of California, Berkeley with Professor Chris Chang, developing fluorescent probes for imaging redox active small molecules. Afterward, she traveled to Switzerland for a postdoctoral fellowship in the...
Category
"DNA Viral Diversity, Abundance, and Functional Potential Vary across Grassland Soils with a Range of Historical Moisture Regimes" Soil viruses are abundant, but the influence of the environment and climate on soil viruses remains poorly understood. Here, we addressed this gap by comparing the...
Category
Soil fungi facilitate the translocation of inorganic nutrients from soil minerals to other microorganisms and plants. This ability is particularly advantageous in impoverished soils, because fungal mycelial networks can bridge otherwise spatially disconnected and inaccessible nutrient hotspots...
Category
Viral communities detected from three large grassland soil metagenomes with historically different precipitation moisture regimes.